A quick guide to 3D product rendering
1. What is 3D product rendering?
3D product rendering is the process of creating 2D images from 3D models. In other words, it’s like taking a photo of a product that exists within your computer software so that it can be easily viewed and shared.
Over the past few years, with the advent of 3D modeling and rendering software, 3D renderings are now more commonly used for marketing and promotional purposes.
Designers, manufacturers, and marketers use 3D product renderings to create photorealistic photos, animations, and interactive 3D models to help explain, promote, and sell products.
The final result of your 3D product rendering may vary based on several factors. Talent, modeling software, and rendering engines all impact the final output
2. How does the 3D product rendering process work?
Rendering is usually the final stage of a 3D project. It involves converting digital models into realistic images or animations. The process begins with creating a 3D model using computer graphics software.
After the 3D model is created, it is loaded into a rendering engine, which calculates lighting, materials, and camera angles and converts the model into a 2D image or animation. After an image is rendered, it is typically post-processed and composited to create the final image or animation.
Let’s review the different steps of the complete 3D product rendering process in more detail.
3. Shape modeling
The modeling process (Modeling) first uses 3D software such as Cinema 4D, Blender, Autodesk 3ds Max or Maya to create a 3D model. Different 3D modeling software offers different solutions, workflows or toolsets, but the end result should usually be the same.
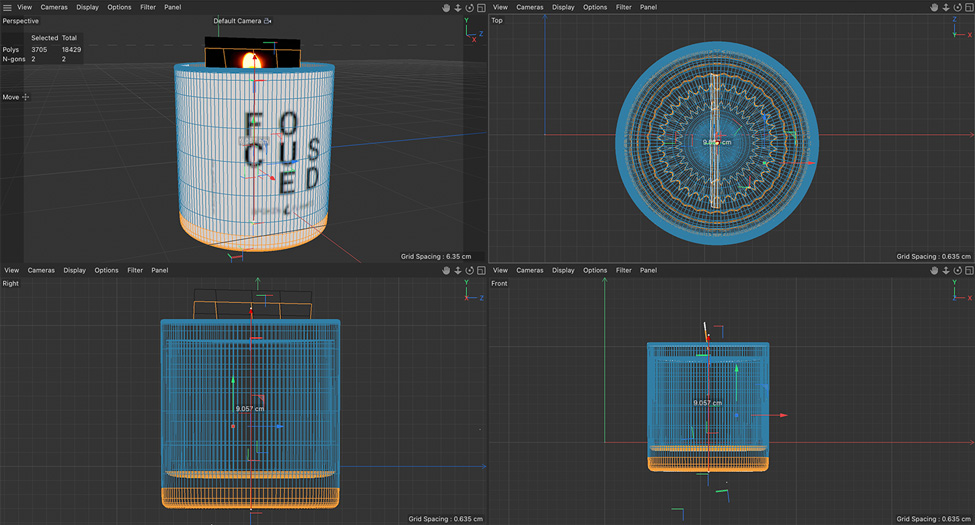
Since 3D models are the basis for 3D product rendering, it is important to note that building 3D models more accurately will yield better results. A good model will make details stand out and look more realistic.
A more accurately built 3D model will also reduce the need to make manual adjustments during the texturing stage to achieve the desired results, saving considerable time and effort.
If you already have 3D models in other formats, such as GLTF, GLB, FBX, OBJ, DAE, etc., you can use this online version of the 3D model conversion tool to convert the 3D model in your hand to the required format.
4. Texturing
Texturing involves adding materials and surface properties to provide visual characteristics to a 3D model and determine how the model interacts with light. Texturing is the process of adding color, pattern, and other important details to a material. This can be done by painting on the surface of the model or applying a texture map to the material.
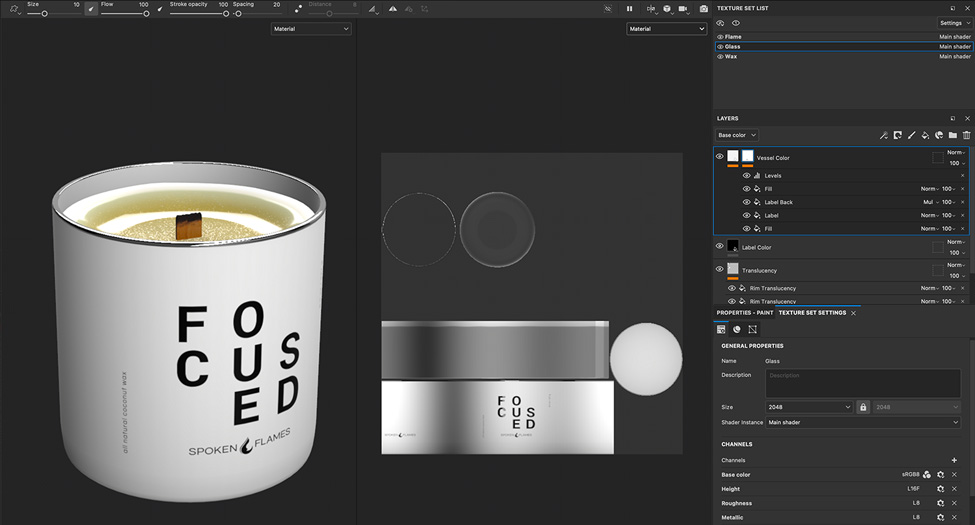
Texture maps are digital images projected onto the surface of a 3D model. Texture maps can be used to project colors and patterns and simulate bumps, scratches, and other surface imperfections. Additionally, maps can be used to add realistic effects such as shadows, reflections, and ambient occlusion.
Materials and textures enable more realistic, detailed 3D visuals and bring flat 3D models to life.
5. Lighting settings
3D lighting (Lighting) works similar to lighting in real environments. Light objects have several properties, such as intensity, color, direction, and attenuation, that affect how the scene is lit. Artists can adjust these properties to control how lights interact with models in the scene.
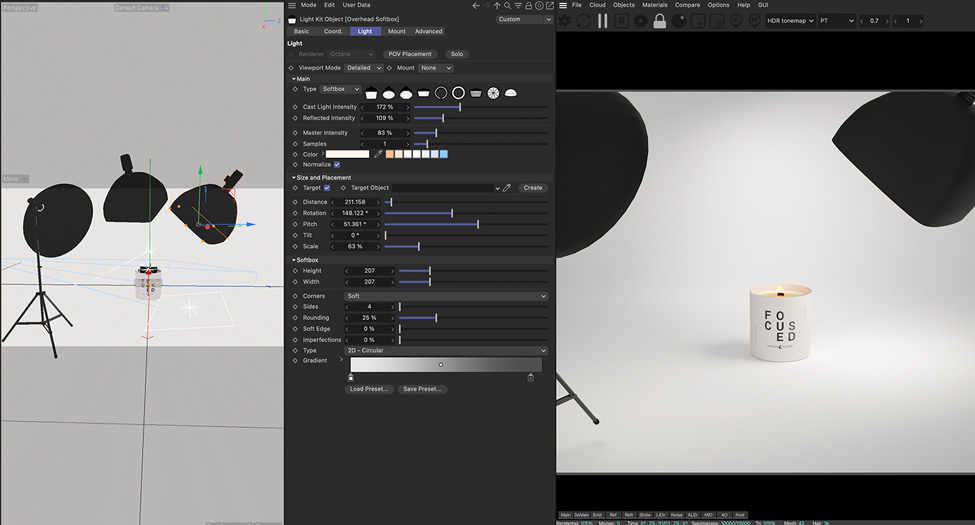
Artists can also create and add different types of lights, such as spotlights, ambient lighting, and point lights, to create specific lighting effects in a scene. This can have a big impact on 3D product renderings.
Combining different types of lights allows the artist to control the overall look and mood of a scene, much like a photographer in a photography studio.
6. Camera settings
Camera setup is an important step before rendering a scene. It’s important to understand how camera settings such as field of view, aspect ratio, focal length, exposure, and other settings affect the appearance of your model. Additionally, the basic rules of photography apply to how you place your camera in a scene.
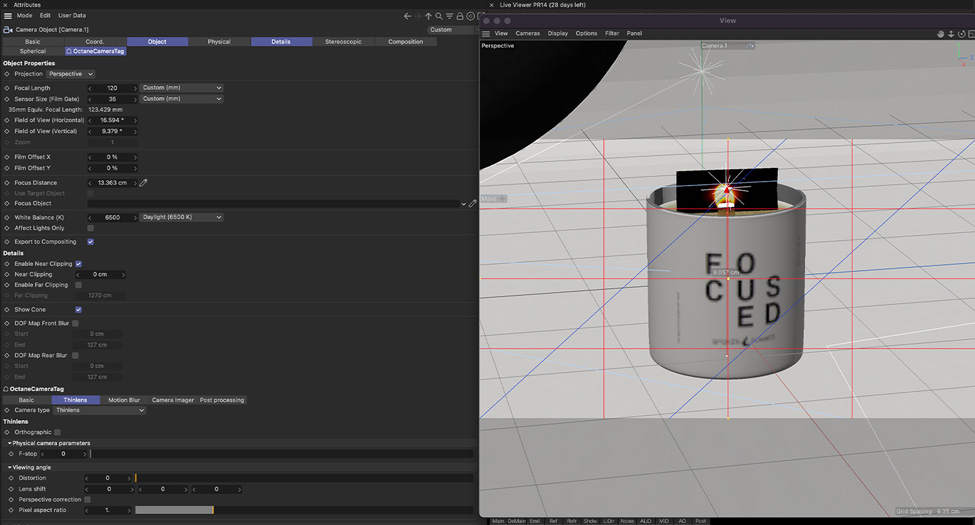
Understanding how camera placement and settings affect scenes and 3D models can help 3D artists create more meaningful, art-directed compositions, set up models that look more natural in 3D environments, and ultimately create more realistic rendered images.
7. Rendering
Rendering is the final process of taking a 3D model and converting it into a 2D image or animation. Rendering involves using various software tools such as 3D modeling, rendering engines, and compositing software.
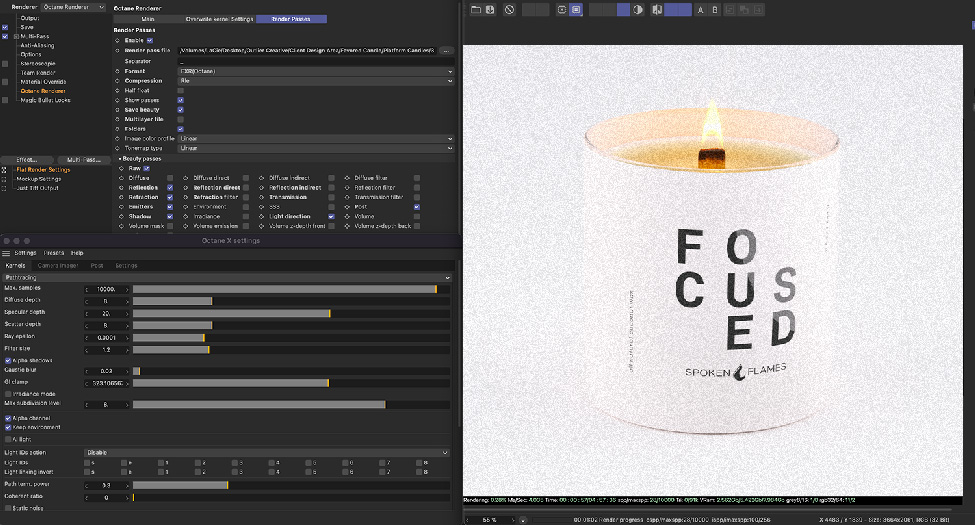
The process can take anywhere from a few minutes to a few days, depending on the complexity of the scene. Once rendered, the image or animation can be used in games, movies, and other media.
8. Post-production
Finally, post-production in 3D modeling is the process of refining and enhancing the rendered image by adjusting colors and adding effects in 2D space. This process is usually done in 2D software such as Photoshop or After Effects. Post-production includes color correction, lighting effects and compositing to create a final, more polished look for the 3D model.
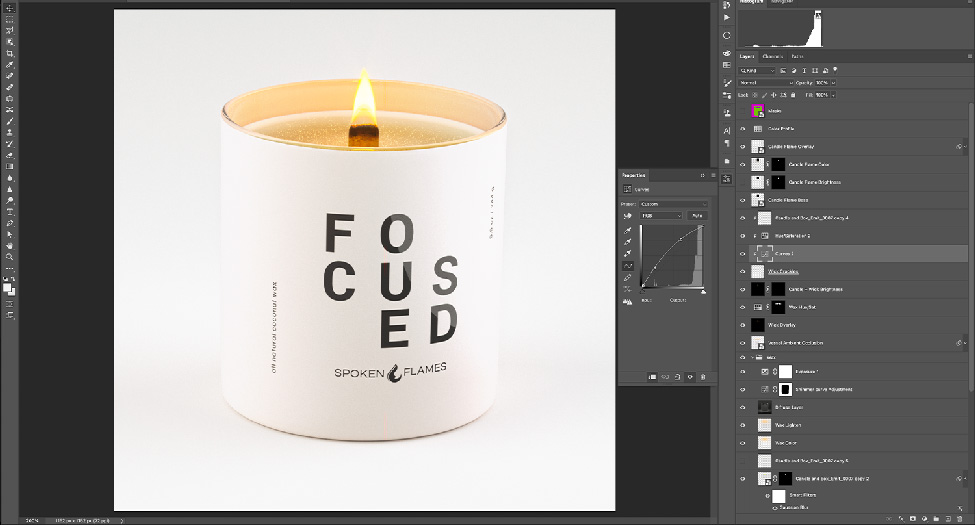
Composition in post-production is the process of combining multiple elements such as reflections, shadows, and ambient occlusion to create the final image or scene. This process helps the artist have greater control over the different elements that put the scene together. Compositing allows artists to easily adjust various properties of individual elements, such as color, brightness, and contrast, and add effects such as light flares and motion blur.
9. How much does 3D product rendering cost?
The cost of 3D product renderings can vary greatly depending on the complexity of the product, the level of detail required, and the time required to create the final product.
Generally speaking, a basic 3D product rendering can cost a few hundred to a few thousand dollars, while a more complex 3D product rendering can cost a few thousand to tens of thousands of dollars.
Texture maps are digital images projected onto the surface of a 3D model. Texture maps can be used to project colors and patterns and simulate bumps, scratches, and other surface imperfections. Additionally, maps can be used to add realistic effects such as shadows, reflections, and ambient occlusion.
Materials and textures enable more realistic, detailed 3D visuals and bring flat 3D models to life.
10. What is needed for 3D product rendering?
To create product renderings that will be used in marketing materials. For example, social media ads, product listings, landing pages, brochures, etc. usually require 5-6 high-quality product photos from different angles and good lighting. If there are technical drawings of the product, using these drawings can make the model more accurate.
11. Can 3D rendering be performed on rotating products?
Yes, rotating products can be 3D rendered using 3D software such as Autodesk 3ds Max, Maya or Blender. The process includes creating a 3D model of the product, setting up lighting and materials, and placing it into the scene. The animation process can then begin, setting up the camera and scene, and creating the rotation animatio
12. What are the uses of 3D product rendering?
- Product design and manufacturing
Most commonly, 3D rendering is used for product prototyping and testing during product manufacturing and to visualize products before they go into production. This gives manufacturers insights into product designs and helps them make necessary adjustments before manufacturing.
3D renderings can also be used to create detailed instructions for assembly processes and create visualizations of products in different environments. This helps manufacturers better understand the product and ensure the final product meets their expectations.
- Marketing and product promotion
Businesses can showcase their products with the help of 3D renderings. Likewise, 3D modeling rendering is becoming more and more common, so it’s no longer just for big movies or brands with big budgets.
These renderings can be used in product advertising, websites or catalogs. 3D renderings allow people to experience a product as closely as possible without actually experiencing it.
- architectural visualization
3D renderings are often used in architecture to help visualize a proposed building or design. They are used to create realistic images of proposed structures that can be used to show clients and other stakeholders what the finished product will look like.
3D renderings can also be used to analyze potential design flaws, identify potential material usage, and evaluate the overall aesthetics of a project. They can also be used to create walkthroughs of the space, allowing clients to experience the design before it is built.
- Special effects in film and television
3D rendering is used for a variety of tasks in special effects and film production. They help create realistic environments, creatures, and objects that would otherwise be difficult or expensive to create in real life.
They can also be used to add extra depth and realism to existing scenes, or to create more realistic environments and objects.
- video games
3D rendering is used to create graphics for video games. They are used to create characters and environments, as well as textures and other elements. They provide a realistic and immersive gaming experience. 3D rendering is also used to create cutscenes and cutscenes in many video games.


